A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. A resistor provides electrical resistance: it limits the flow of the electrons through the circuit. In this video, we’re going to learn about how resistors work! We’ll explore the different types of resistors, how resistors work in circuits, and how to calculate resistance.
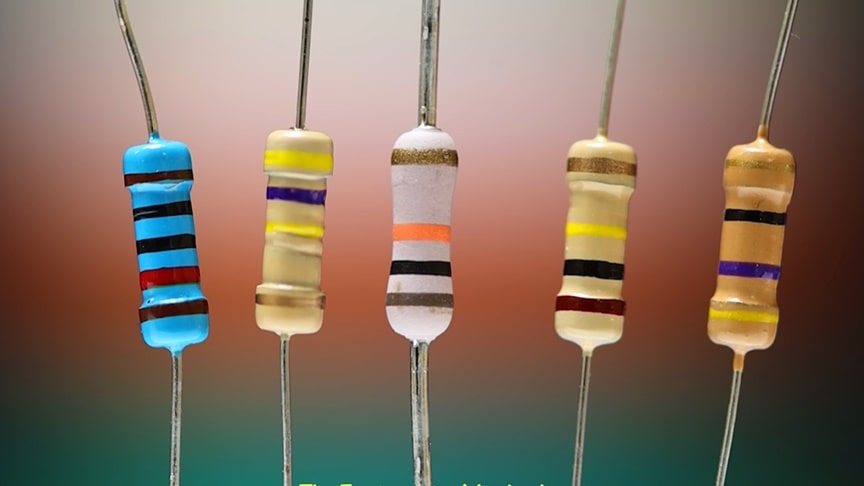

source.image: The Engineering Mindset
Resistors are useful for a few reasons. First, allowing electricity to flow from the positive charge to the negative charge without anything to stop it, causes a big safety risk known as a short circuit. The resistor moderates the flow of electrons, so the current doesn’t move too quickly and cause damage to the breadboard, wires, battery, etc. The second reason to use a resistor is to slow the current flow to a component.
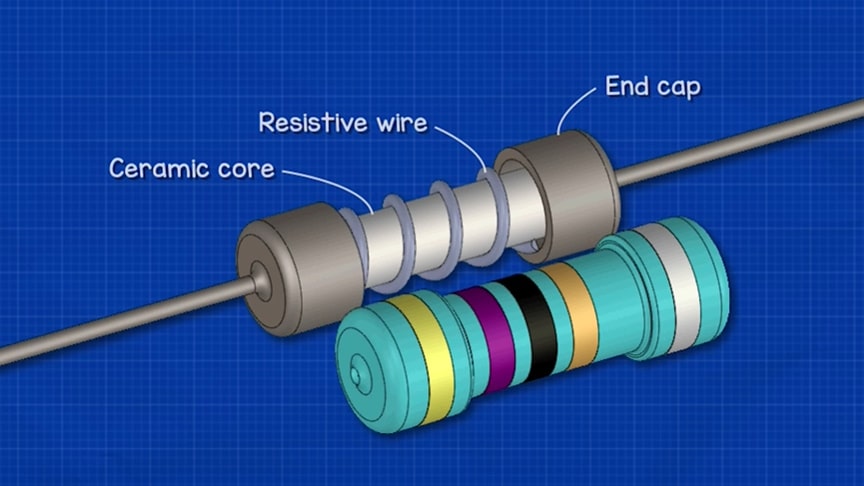
source.image: The Engineering Mindset
The resistor absorbs the electrical energy in the process where it acts as a hindrance to the flow of electricity by reducing the voltage, and it is dissipated as heat.In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
Advertisement
High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage.
Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.Components like LED’s, fans, light bulbs, etc. are designed to function with a certain amount of electrical current. Too little and they won’t work, too much and you can damage or destroy the component.









